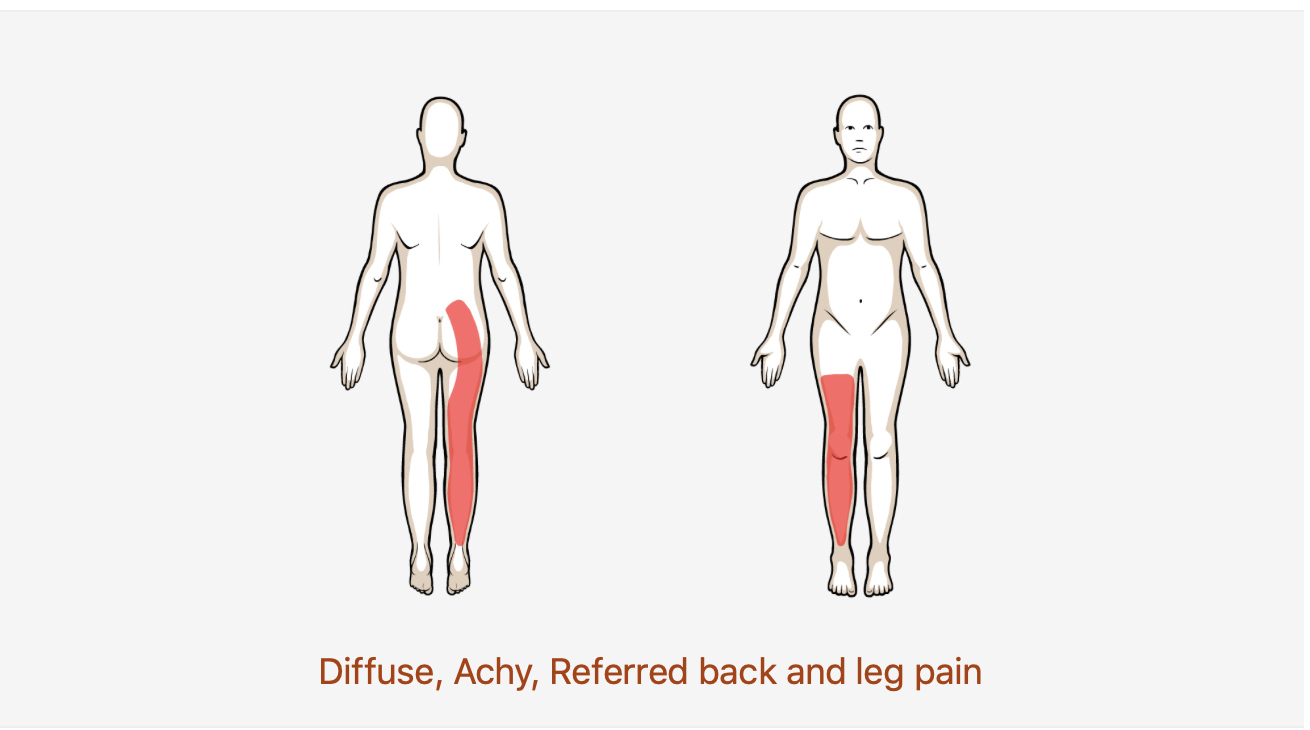
Lower Back Pain with Radiating Pain
Not to be confused with lower back pain with related leg pain; patients with a disc herniation will be more likely to have complaints of narrow shooting/burning type pain sometimes associated with numbness. It is important for the Physical Therapist to be able to make the distinction between the two.
If you do not know the common clinical findings no problem! Click here
Anatomy
Image via Complete Anatomy 2018 by 3D4 Medical
Common Movement Fault
Similar to disc disorders due to displacement, typical mechanism of injury associated with discogenic herniation is bending forward to lift (often times heavy) objects. If the patient moves too readily through the lumbar spine and not enough through the hip (flexion movement fault), they are at a higher risk for back injury! (Click image to watch 1-2 minute video)
Special Tests
The straight leg raise is an excellent for ruling out disc herniation due to it’s high sensitivity (0.97)! (Click image to watch 1-2 minute video)
Treatment
It is important to note that in the early stages of disc herniation rehabilitation, the centralization procedures used for treating lower back pain with related leg pain may actually cause symptom exacerbation. Patient’s who present to clinic with an acute injury or high irritability may benefit from finding positions of comfort, maintaining neutral spine alignment, and slow restoration of normal lumbar spine lordosis. (Click the image to watch 1-2 minute video)
Therapeutic Exercise
The quadruped rock back is an excellent exercise for this patient population. It puts the lumbar spine in a gravity eliminated position and teaches the patient how to move through their hips while maintaining a neutral lumbar spine! (Click image to watch 1-2 minute video)